Benefits of Chili

Benefits of
Chili

Capsaicin is the active component found in chili peppers, and it's known for its heat-producing properties. Capsaicin has been found to be very effective in relieving muscle pain and inflammation through several mechanisms:
1. Desensitization of Nerves:
Capsaicin works by binding to and activating a receptor called the transient receptor
potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) receptor. This receptor is responsible for sensing heat and pain. When capsaicin binds to TRPV1, it reducing the transmission of pain signals to the
brain. This desensitization effect can provide relief from muscle pain.
2. Release of Substance P:
Capsaicin triggers the release of substance P, which is a neuropeptide involved in transmitting pain signals. Capsaicin helps to reduce the substance P levels ,
leading to a reduction in pain sensation.
3. Anti-inflammatory Effects:
Capsaicin contains strong anti-inflammatory properties. It can inhibit the production of
inflammatory cytokines in the affected muscles or joints andpromotes healing.
4. Increased Blood Flow:
Capsaicin has vasodilatory effects, meaning it can widen blood vessels. This increased blood flow to the affected area can help reduce inflammation by flushing out inflammatory mediators and bringing in nutrients and oxygen necessary for tissue repair.
5. Muscle Relaxation:
Capsaicin can also act as a muscle relaxant, helping to relieve tension and stiffness in muscles.
6. Long-Term Pain Relief:
Studies have suggested that the pain-relieving effects of capsaicin can extend beyond the
period of its application. Regular use of capsaicin-containing products may lead to long-term pain relief by modulating pain perception and reducing inflammation.
Capsaicin is the active component found in chili peppers, and it's known for its heat-producing properties. Capsaicin has been found to be very effective in relieving muscle pain and inflammation through several mechanisms:
1. Desensitization of Nerves:
Capsaicin works by binding to and activating a receptor called the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) receptor. This receptor is responsible for sensing heat and pain. When capsaicin binds to TRPV1, it reducing the transmission of pain signals to the
brain. This desensitization effect can provide relief from muscle pain.
2. Release of Substance P:
Capsaicin triggers the release of substance P, which is a neuropeptide involved in transmitting pain signals. Capsaicin helps to reduce the substance P levels, leading to a reduction in pain sensation.
3. Anti-inflammatory Effects:
Capsaicin contains strong anti-inflammatory properties. It can inhibit the production of inflammatory cytokines in the affected muscles or joints andpromotes healing.
4. Increased Blood Flow:
Capsaicin has vasodilatory effects, meaning it can widen blood vessels. This increased blood flow to the affected area can help reduce inflammation by flushing out inflammatory mediators and bringing in nutrients and oxygen necessary for tissue repair.
5. Muscle Relaxation:
Capsaicin can also act as a muscle relaxant, helping to relieve tension and stiffness in muscles.
6. Long-Term Pain Relief:
Studies have suggested that the pain-relieving effects of capsaicin can extend beyond the period of its application. Regular use of capsaicin-containing products may lead to long-term pain relief by modulating pain perception and reducing inflammation.

FEEL BETTER TODAY WITH
Re-liv Magnesium Oil Lotion
Natural pain relief and muscle relaxation for total wellness.
FEEL BETTER TODAY WITH
Re-liv Magnesium
Oil Lotion
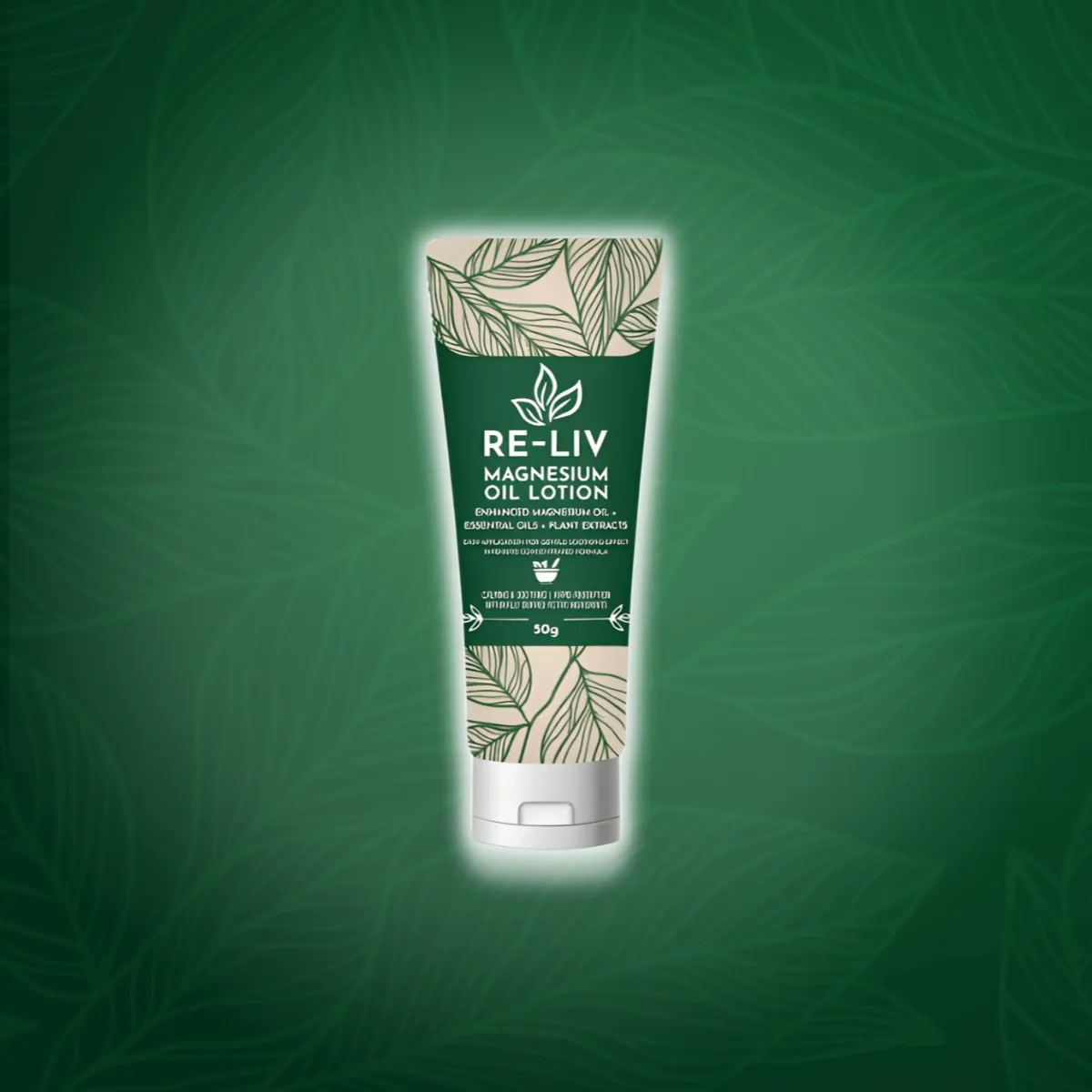

Natural pain relief and muscle relaxation for total wellness.
Science-Backed
Effective Relief

